Enhanced Due Diligence: Navigating the measures to manage high-risk under Singapore AML Laws
Enhanced Due Diligence: Navigating the measures to manage high-risk under Singapore AML Laws
The regulated entities engage with different customers every day, coming from different jurisdictions from various business profiles, posing different levels of money laundering or terrorism financing exposure. The AML regulations in Singapore mandate the regulated entities to apply adequate customer due diligence measures depending on the customer’s risk profile. The law prescribes adopting Enhanced Customer Due Diligence when engaging with high-risk customers, i.e., the business relationships or the transaction construed as posing an increased risk of financial crime.
In this article, let us explore Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), the measures there under, the circumstances when EDD is performed, and its significance under AML Singapore regulations.
What is Enhanced Due Diligence?
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) is a type of customer Due Diligence comprising extensive measures applied to establish the customer’s identity when the assessed risk arising from such customer or business relationship is high.
EDD is an extension of the Standard Customer Due Diligence, generally followed in the case of normal customers, categorized under low or medium-risk levels. During EDD, the regulated entities dive deep into the customer’s background to detect potential red flags suggesting involvement in money laundering or terrorism financing attempts. In addition to the basic due diligence related to identifying and verifying the identity, EDD involves additional inquiry and review around the customer, their purpose of establishing the business relationship, their financial profile, etc.
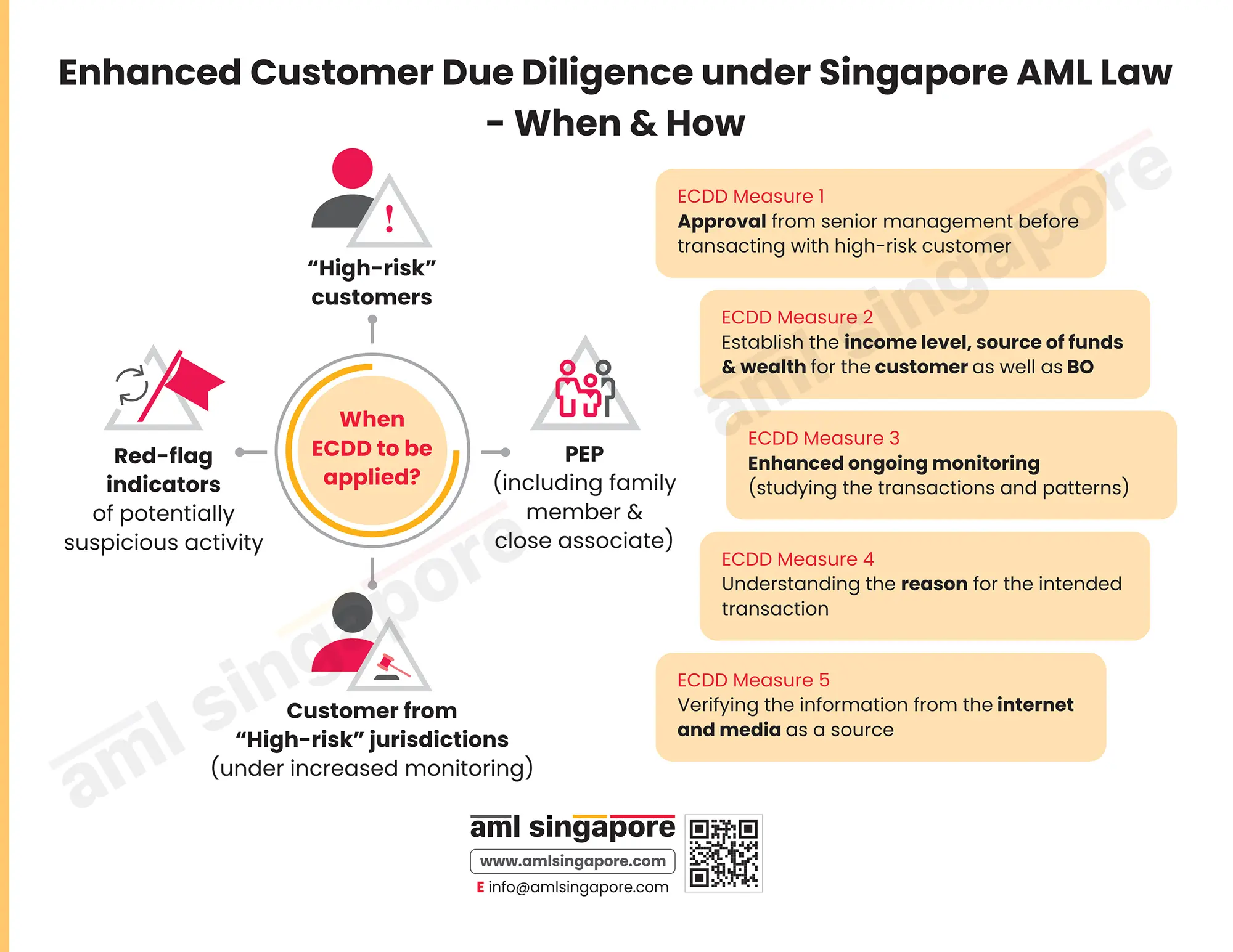
What are the circumstances when Singapore AML regulation mandates the performance of EDD?
The AML regulations of Singapore provide for the following circumstances when the customer would be classified as “high-risk”, warranting the regulated entity to implement the Enhanced Due Diligence process:
- When the customer comes from or is closely associated with the countries subject to FATF’s Call for Action, either apply the countermeasures or adopt enhanced measures to manage the risk (FATF Blacklist).
- When the customer is a resident of or has business connections with jurisdictions with inadequate regulatory frameworks to combat money laundering and terrorism financing or countries notorious for financial crimes or high levels of corruption.
- When the customer or the beneficial owner is a Politically Exposed Person (PEP) or is a close associate or a family member of a PEP. (It is important to note that in case of a domestic PEP or a person holding a prominent public function in any international organization, such customer shall, by default, not be treated as high-risk unless any unusual activity is detected or any other risk indicator suggests otherwise).
- When any concerned authority has notified the person as posing an increased risk of money laundering or terrorism financing.
In addition to the above, if the regulated entity observes any other red flag or potential risk indicator requiring the customer to be classified as high-risk, adequate enhanced due diligence measures must be applied in proportion to the risk assessed.
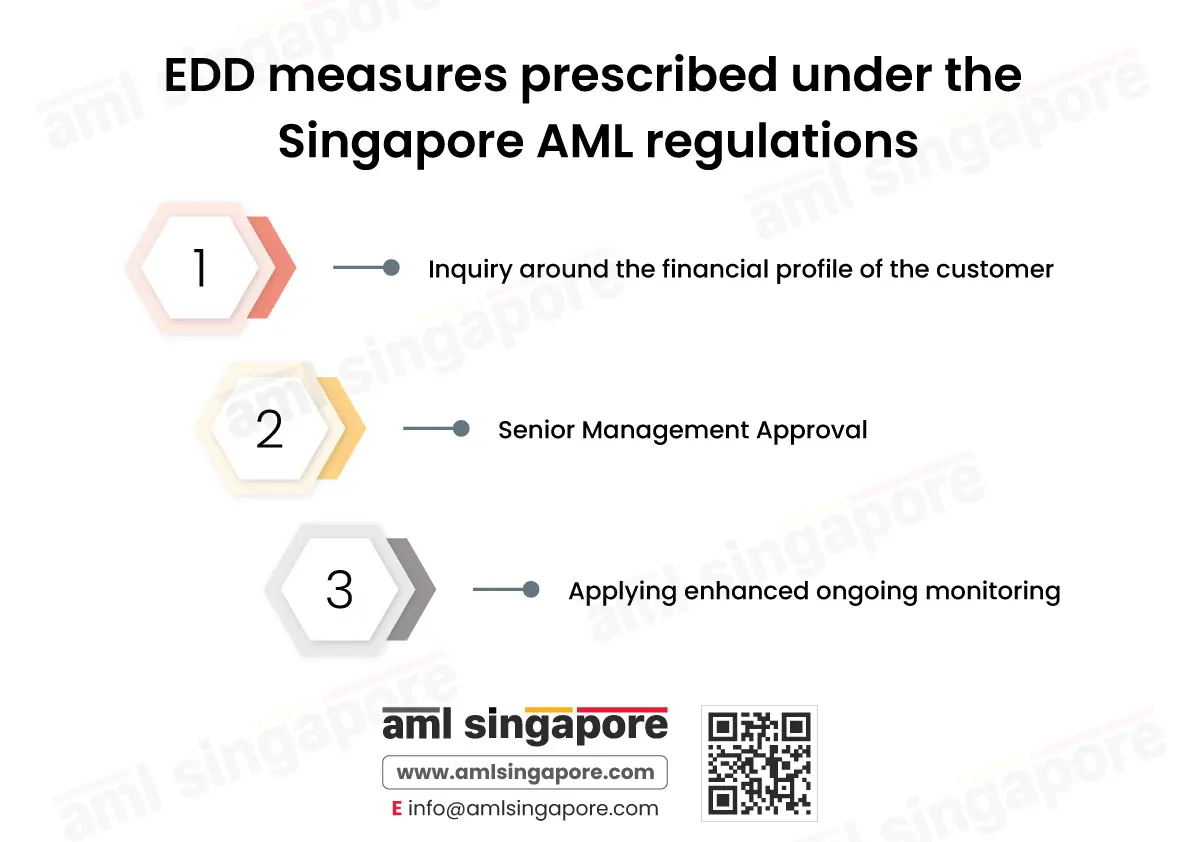
What are the EDD measures prescribed under the Singapore AML regulations?
To manage the increased risk of financial crime, the EDD program crafted by the regulated entity must be comprehensive and focused on detecting any malicious intention of the customer to exploit the business for laundering funds or financing terrorist activities. The EDD measures that must form part of the entity’s EDD framework are as follows:
1. Inquiry around the financial profile of the customer:
When a potential customer is identified as high-risk, the inquiry must be made around the funds involved in the transactions and the nature of the customer’s income to establish whether such amount is in any way connected with any financial crime. As part of EDD, the regulated entities must make reasonable efforts to understand the customer’s income level and the nature of the source of funds and wealth and try to determine its legitimacy using reliable sources like salary slips, annual financial statements, or tax returns. In the case of a corporate customer, the regulated entities must apply these measures to check the financial profile of the
beneficial owners as well, as they are the real persons pumping in the funds or navigating the transactions. Here, the source of funds would mean the origin of the funds or the amount involved in the particular transaction. While the source of wealth indicates the origin of the accumulated assets or resources of the customer.
2. Senior Management Approval:
The senior management of the regulated entity must be aware of the increased risk that a customer or a transaction poses to the business. For this, the Singapore AML regulations require that the regulated entities seek senior management approval when a business relationship is proposed to be established with a high-risk customer.
Moreover, senior management approval is also required in the case of an existing customer when the customer’s risk classification changes during the ongoing business relationship. This approval must be obtained before executing any further transaction with the customer, i.e., continuing the existing relationship.
3. Applying enhanced ongoing monitoring:
It is essential to track its profile and the transactions in the course of an established business relationship to detect any red flags or suspicious activities promptly. The frequency and the degree of such ongoing monitoring must be increased in case of high-risk customers subject to Enhanced Due Diligence. Here, the regulated entities may implement a policy to periodically select certain transactions of high-risk customers that would be thoroughly investigated to check their validity.
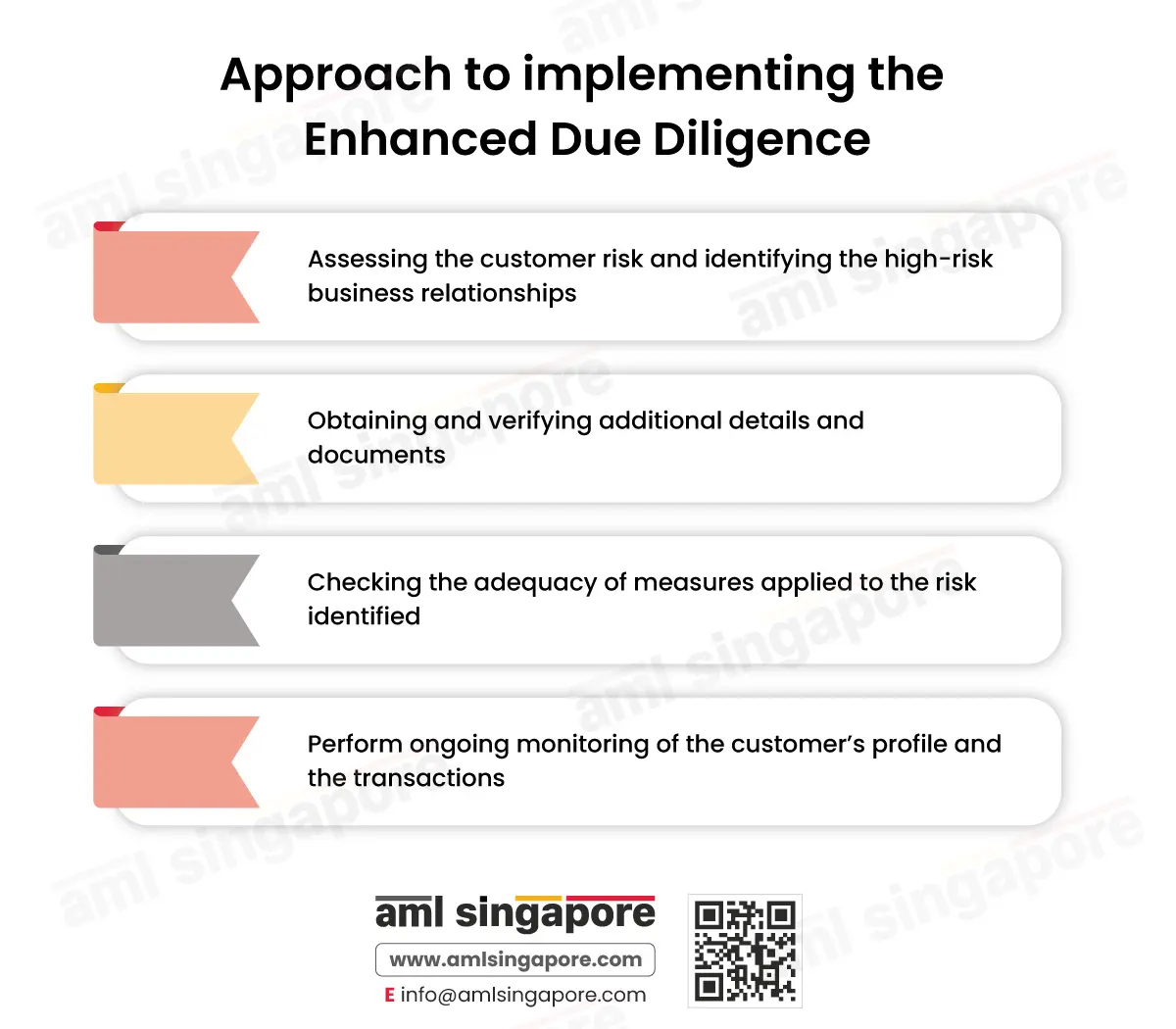
Approach to implementing the Enhanced Due Diligence
Having developed a robust Enhanced Customer Due Diligence program, it is equally important to adopt the right approach to ensure the effectiveness of the EDD measures. A systematic approach, as mentioned hereunder, will help the regulated entities in managing the high ML/FT exposure and staying compliant with the Singapore AML regulations:
Assessing the customer risk and identifying the high-risk business relationships:
The foundation of the EDD program is that the regulated entity has classified a customer or a business relationship as high-risk. The entity must adopt a holistic approach while determining a customer’s risk profile, considering various factors like the location of the customer, its business activities, the intended nature of the business relationship, etc.
Obtaining and verifying additional details and documents:
Once high-risk customers or transactions are identified, the regulated entities must obtain additional information and documents from the customer. The authenticity of the received details and documents must be verified.
Checking the adequacy of measures applied to the risk identified:
Having applied the additional measures and checks, the regulated entity must assess whether these measures align with the customer’s increased risk and whether the Customer Due Diligence process can be construed to have been satisfactorily concluded. If the regulated entity still believes that the measures do not appropriately manage the risk, the entity must consider applying stringent measures, if possible; otherwise, reject the customer and explore the requirement to report the person by filing a Suspicious Transaction Report (STR).
Perform ongoing monitoring of the customer’s profile and the transactions:
Once the high-risk customer is onboarded, the regulated entity must subject this customer and the transactions monitoring to ongoing monitoring to detect any suspicious customer behaviour or transaction inconsistent with the customer’s overall profile. If any red flags suggest the customer’s involvement with financial crime or attempts to launder the funds, the regulated entities must timely report the same to the authorities by filing a suspicious Transaction Report.
By thoroughly adopting the enhanced due diligence process, the regulated entities can efficiently detect and prevent financial crime while staying compliant with the AML regulations in Singapore.
Why is EDD a significant element of the AML Program?
Enhanced Due Diligence, though it may be treated as an additional exercise requirement for more resources, is essential, making a significant impact on the regulated entities’ efforts to combat financial crimes, which are as follows:
- When the regulated entity implements the EDD program, it demonstrates the commitment and dedication of the business in fighting money laundering and terrorist financing. It enhances the government and the customer’s trust and confidence in the business.
- With more strict measures and checks, the regulated entities can control the financial criminals sneaking into the business to achieve their criminal objectives. It saves the business from commercial loss and also avoids reputational damages.
- When EDD measures are not applied for customers posing higher ML/FT risks, the same tantamount to regulatory non-compliance results in huge fines and penalties. It also adversely impacts the regulated entity’s reputation in the market.
In the interest of the business, it is inevitable for the business to design and maintain a robust Enhanced Due Diligence program to manage the risk, protect the business, and stay AML compliant.
Let AML Singapore assist you in designing your Enhanced Due Diligence program.

About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 26 years of experience in governance, risk, and compliance. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from conducting Enterprise- Wide Risk Assessments to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework. He has played a pivotal role as a functional expert in developing and implementing RegTech solutions for streamlined compliance.