AML Compliance for Registered Filing Agents in Singapore
AML Compliance for Registered Filing Agents in Singapore
Registered Filing Agents (RFAs) or Corporate Service Providers (CSPs) in Singapore are subject to Anti-Money Laundering, Countering Financing of Terrorism and Counter-Proliferation Financing (AML, CFT, and CPF) guidelines issued by the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA).
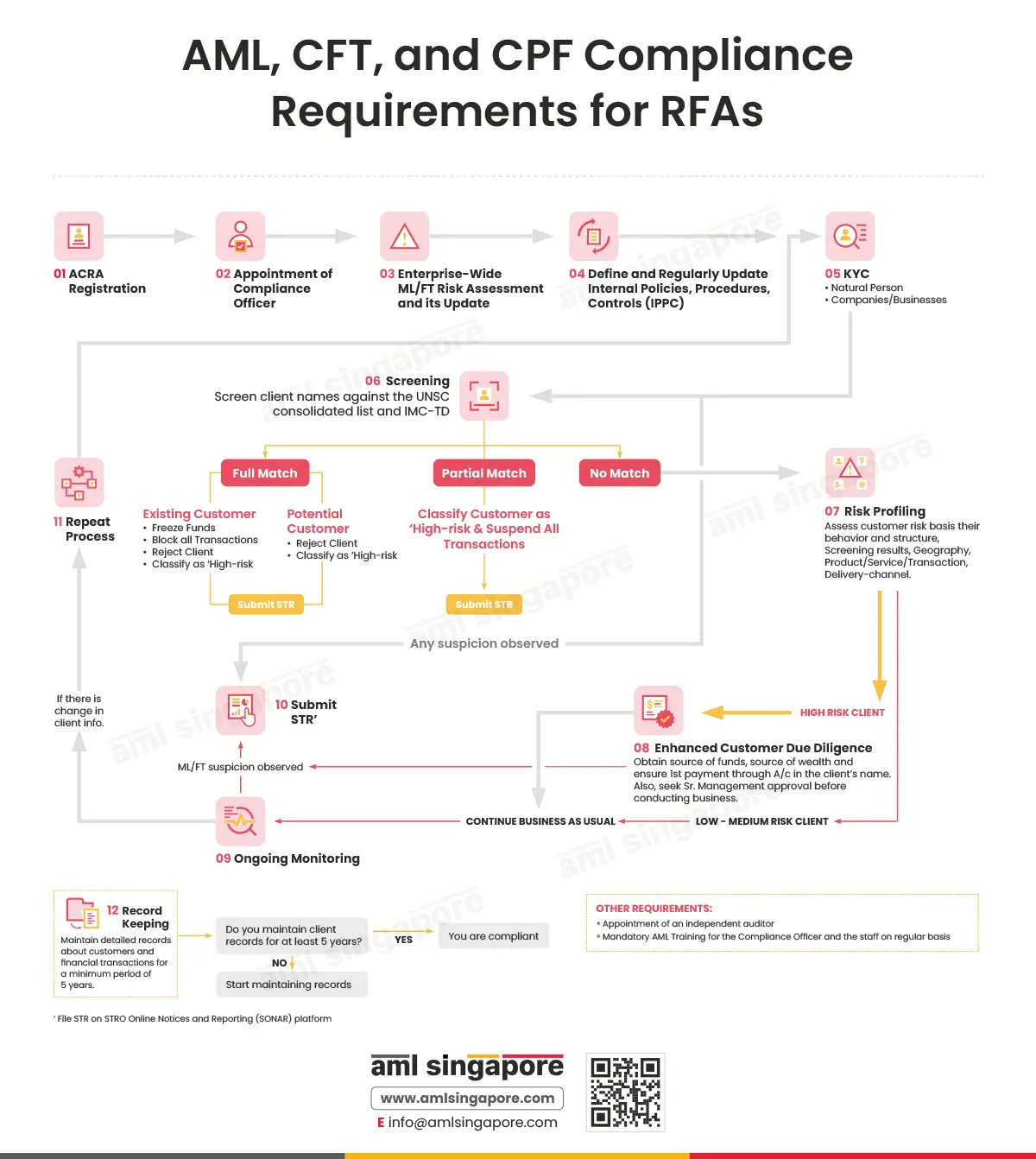
This illustration provides a step-by-step guide to the AML, CFT, and CPF requirements for Registered Filing Agents.
- Registering with the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority ACRA as a registered CSP.
- Appointing an AML compliance officer for effective implementation of the Internal Policies, Procedures, and Controls (IPPC).
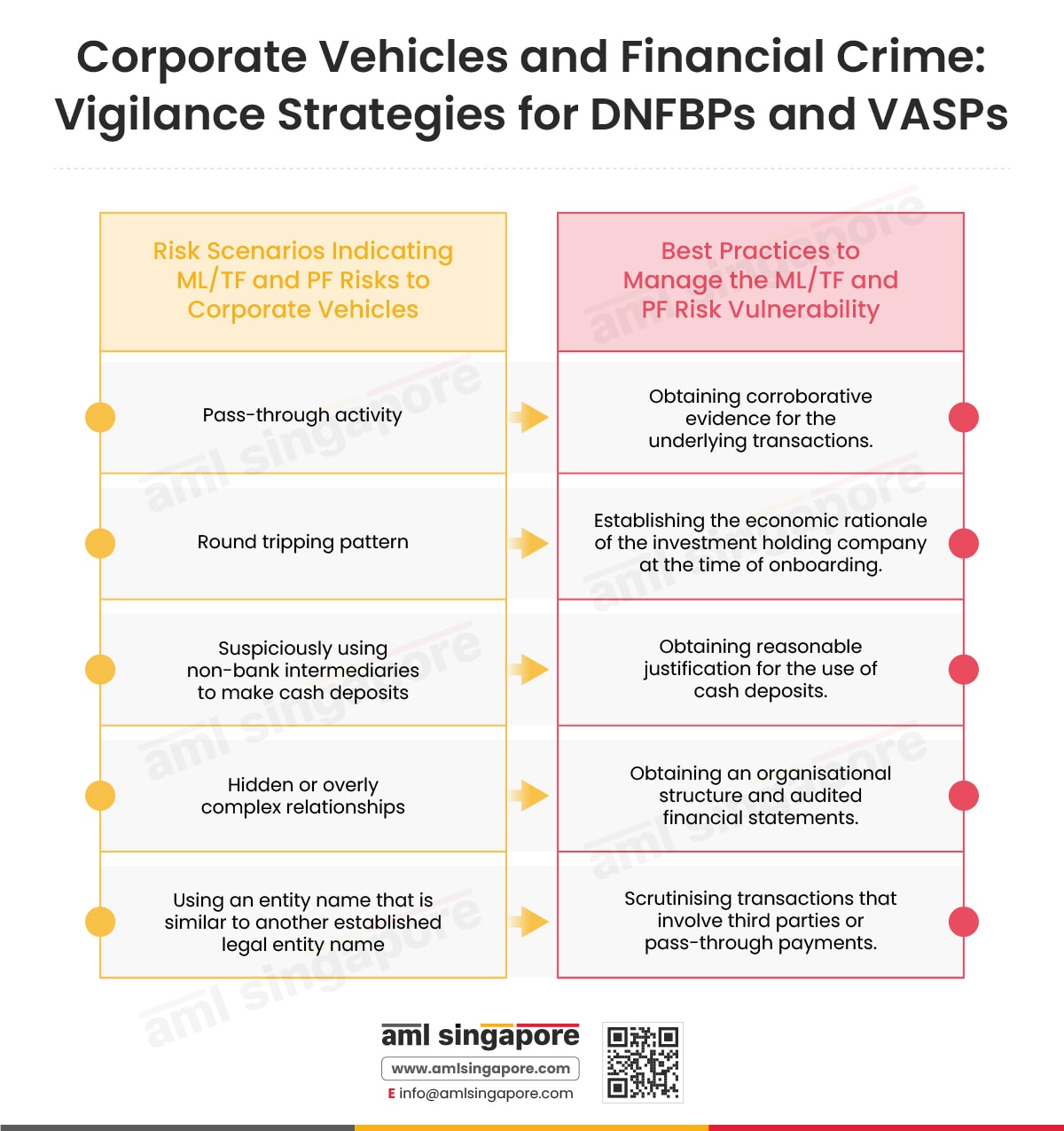
- Conducting Enterprise-Wide ML/FT Risk Assessment to identify the ML/FT risk vulnerabilities to the RFA relating to the services or products offered by the RFA or the risks associated with the jurisdiction that the RFA works with or operates in.
- Documenting detailed Internal Policies, Procedures, and Controls (IPPC) and periodically updating them to prevent ML, FT, and PF activities.
- Adopting the Know Your Customer (KYC) process to verify customer, agent, beneficial owner and connected party’s identification information and documentation
- Conducting Name Screening to verify if the customer or beneficial owner is a designated individual or entity or a Politically Exposed Person (PEP). Name Screening can additionally be done to verify if there are any adverse media articles against the customer or beneficial owner
- Undertaking Customer Risk Assessment and Customer Risk Profiling to classify the customer into high-risk, medium-risk, and low-risk based on factors like residential status, legal nature, nature of business undertaken by the customer, etc.
- Based on the Customer Risk Assessment, the RFA should determine the extent of due diligence measures to be implemented. For instance, Performing Enhanced Customer Due Diligence for high-risk customers. The enhanced measures should correspond to the nature of enhanced risk factors. For example, when dealing with non-face-to-face customers, additional information, data or documentation should be sought. While dealing with a PEP, enhanced measures must be adopted to identify the source of wealth and source of funds.
- Conducting Ongoing Monitoring of transactions and business relationships for continued protection against ML/TF risks.
- Timely reporting of suspicious activity or transactions by filing a Suspicious Transaction Report (STR) to Singapore’s Suspicious Transaction Reporting Office (STRO) using the SONAR platform.
- Repeating the process if there is any change in the customer information.
- Maintaining all the relevant AML compliance records and supporting documents in their original format, along with their photocopies and electronic versions, for a minimum period of five years in such a manner that the records are readily available for ACRA inspection.
Fulfilling AML, CFT, and CPF Obligations
In conclusion, a methodological approach to AML, CFT, and CPF compliance can help Registered Filing Agents ensure that they never fall short of ACRA’s expectations.
Related Posts

Worried about your Company’s AML Compliance Requirements?
Let go of all your business-related compliance concerns with AML Singapore.