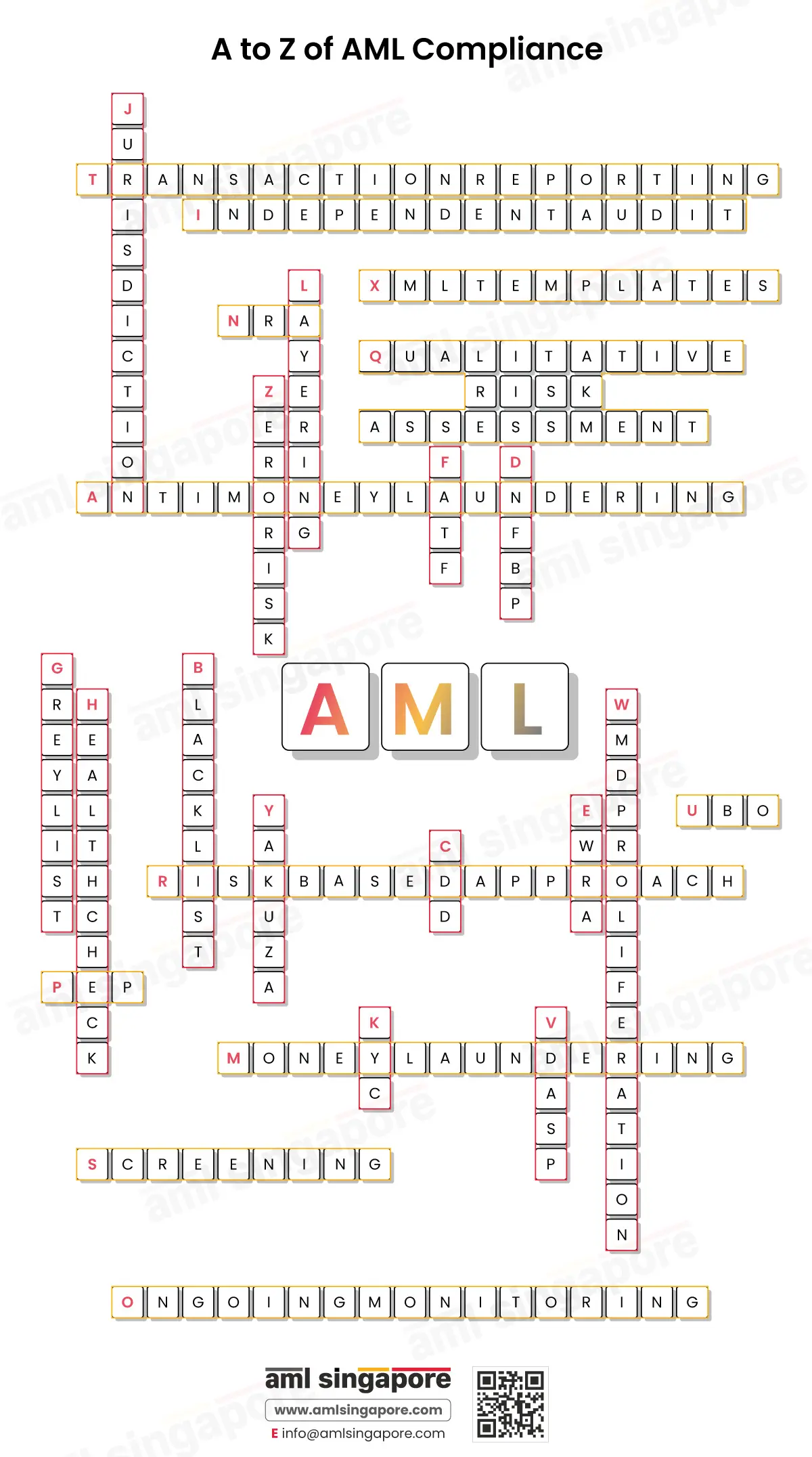
The A to Z of AML Compliance
The puzzle of AML compliance can be challenging to solve. This illustration is a guide to understanding key AML terms to kickstart a business’s AML compliance journey.
| Letter | Term | Description |
| A | Anti-Money Laundering (AML) | A series of laws, regulations, and procedures to prevent conversion of dirty money into legitimate income |
| B | Blacklist | Countries with serious strategic deficiencies to counter Money Laundering, Terrorism Financing, and Proliferation Financing (ML/TF/PF) risk are classified as high-risk jurisdictions by FATF on the Blacklist |
| C | Customer Due Diligence (CDD) | It is a regulatory requirement that includes KYC, Sanctions Screening, Customer Risk Assessment, Enhanced Due Diligence and Ongoing Monitoring |
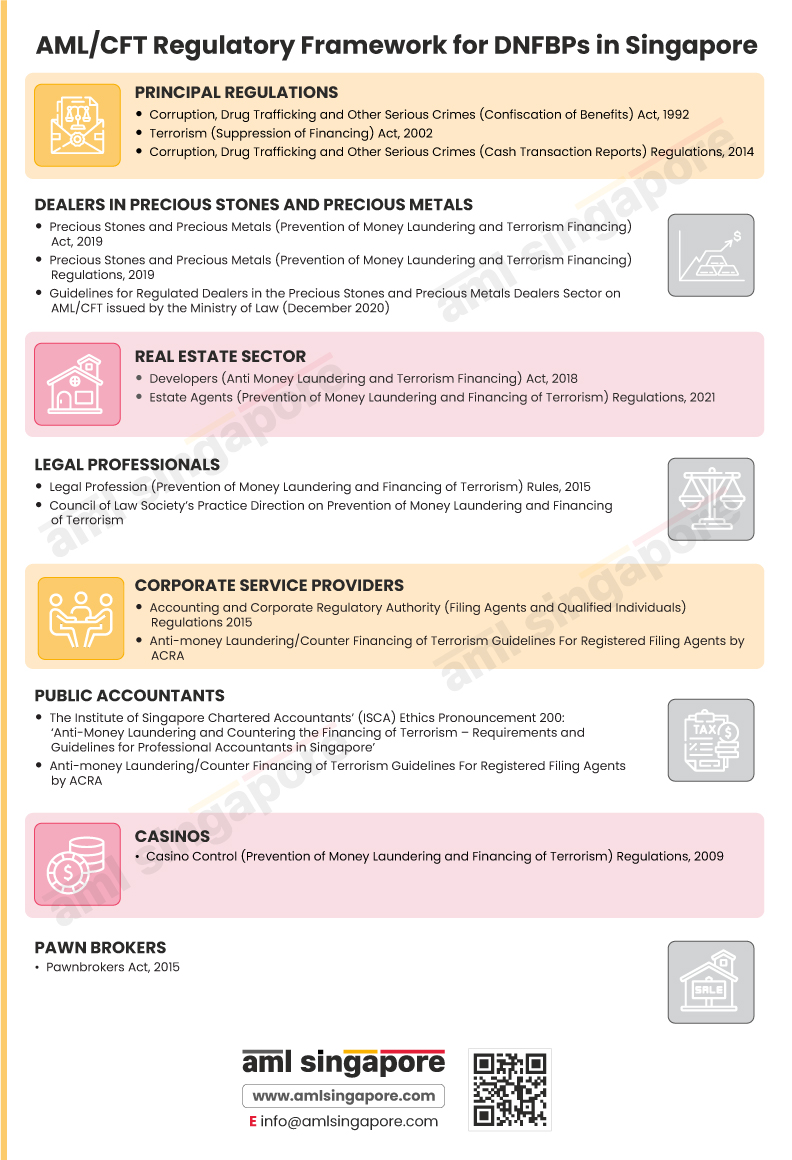
| D | Designated Non-Financial Businesses and Professions (DNFBPs) | Businesses that play a significant role in the financial system and are also likely to encounter ML/TF/PF risks, such as Lawyers, Public Accountants, Real Estate Agents and Developers, Precious Stones and Precious Metals Dealers |
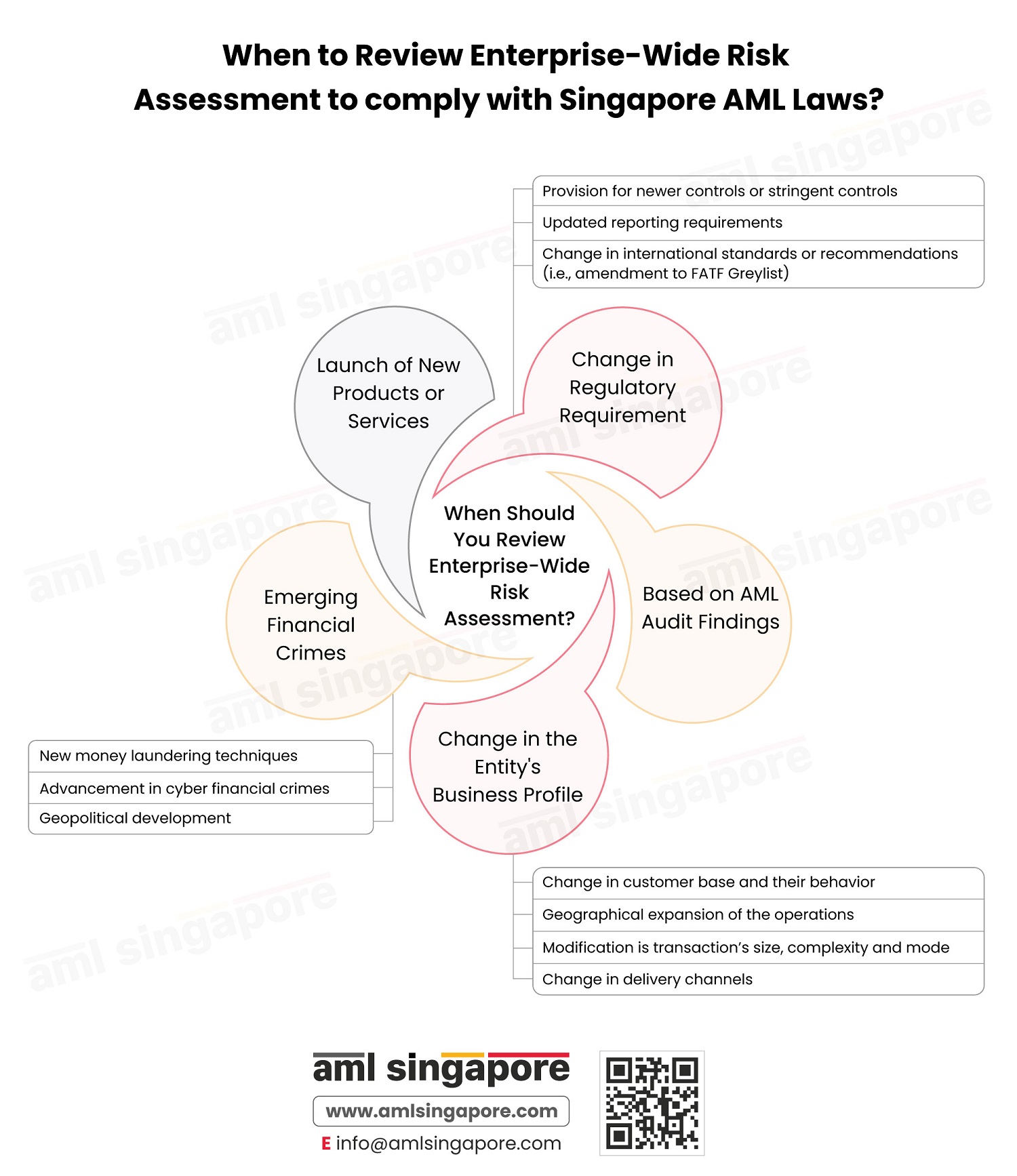
| E | Enterprise-Wide Risk Assessment (EWRA) | The process of identifying the overall ML/TF/PF risk to the business |
| F | Financial Action Task Force (FATF) | An international body for collaborative action against ML/TF/PF activities |
| G | Grey List | Countries that are put under enhanced monitoring but are closely working with the FATF to address their strategic deficiencies are put under the Grey List |
| H | Health Check | Health check of a business includes reviewing the existing AML processes, policies and controls |
| I | Independent Audit | An AML compliance obligation that provides an objective, impartial and unbiased review of AML/CFT controls |
| J | Jurisdiction Under Increased Monitoring | A jurisdiction under increased monitoring is a country identified by the FATF as having weaknesses in its AML/CFT framework and is being closely monitored while addressing these issues, often referred to as being on the “Grey List” |
| K | Know Your Customer (KYC) | A systematic process of collecting customer data and verifying them against reliable information sources and documents |
| L | Layering | The middle stage of money laundering, where multiple layers of transactions occur to disguise the origin of illegal funds |
| M | Money Laundering (ML) | The process of making illegal proceeds of a predicate offence appear legitimate |
| N | National Risk Assessment (NRA) | A comprehensive report of major ML/TF/PF risks to the financial system of the country |
| O | Ongoing Monitoring | The process of continuous assessment of client behaviour and transactions in the course of a business relationship for any suspicious activity that may suggest ML/TF/PF risks |
| P | Politically Exposed Person (PEP) | Persons entrusted with a prominent public function in a domestic or foreign country who can exercise control or influence the economic or political decisions of that country |
| Q | Qualitative ML/TF Risk Assessment | ML/TF risk assessment focused on qualitative aspects of controls, i.e. their appropriateness and effectiveness. |
| R | Risk-Based Approach (RBA) | The process of identifying and assessing inherent risk, implementing the necessary risk mitigation measures, and quantifying residual risk in accordance with the business’s risk appetite |
| S | Sanctions Screening | A regulatory requirement of matching the client’s name against domestic and international sanctions lists to check if the client is a designated individual |
| T | Transaction Reporting | Suspicious Transaction Reporting (STR) and Cash Transaction Reporting (CTR) are regulatory requirements that help the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) in detecting ML/TF/PF and other serious offences |
| U | Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO) | Natural persons who ultimately own or exercise interest or control over a legal entity |
| V | Virtual Digital Asset Service Providers (VDASPs) | Any natural or legal person whose business activities involve an exchange between virtual assets and fiat currencies or one or more forms of virtual assets, storage, administration or transfer of virtual assets, or participation in and provision of financial services related to the offer or sale of virtual assets |
| W | Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) Proliferation | Illegal manufacturing, acquisition, possession, development, export, trans-shipment, brokering, transport, transfer, stockpiling, delivery or use of nuclear, chemical, or biological weapons and related materials |
| X | XML Templates: | XML templates are used by regulated entities to report suspicious activities and transactions to the FIU. |
| Y | Yakuza | The Yakuza, also known as gokudō, are members of organised crime groups that originated in Japan and operate internationally. While the Japanese police and media refer to them as bōryokudan, meaning “violent groups,” the Yakuza prefer to call themselves ninkyō dantai, or “chivalrous organisations. |
| Z | Zero Risk | There is no such thing as zero risk in managing ML/TF/PF risks. A risk-based approach is essential to determine whether the residual risk aligns with the firm’s risk appetite. |
The list of AML key terminologies is endless, but the A to Z of AML compliance are the building blocks of an effective AML program.