A Guide to Avoiding the Top 6 AML Record-Keeping Mistakes
A Guide to Avoiding the Top 6 AML Record-Keeping Mistakes
Singapore AML regulations
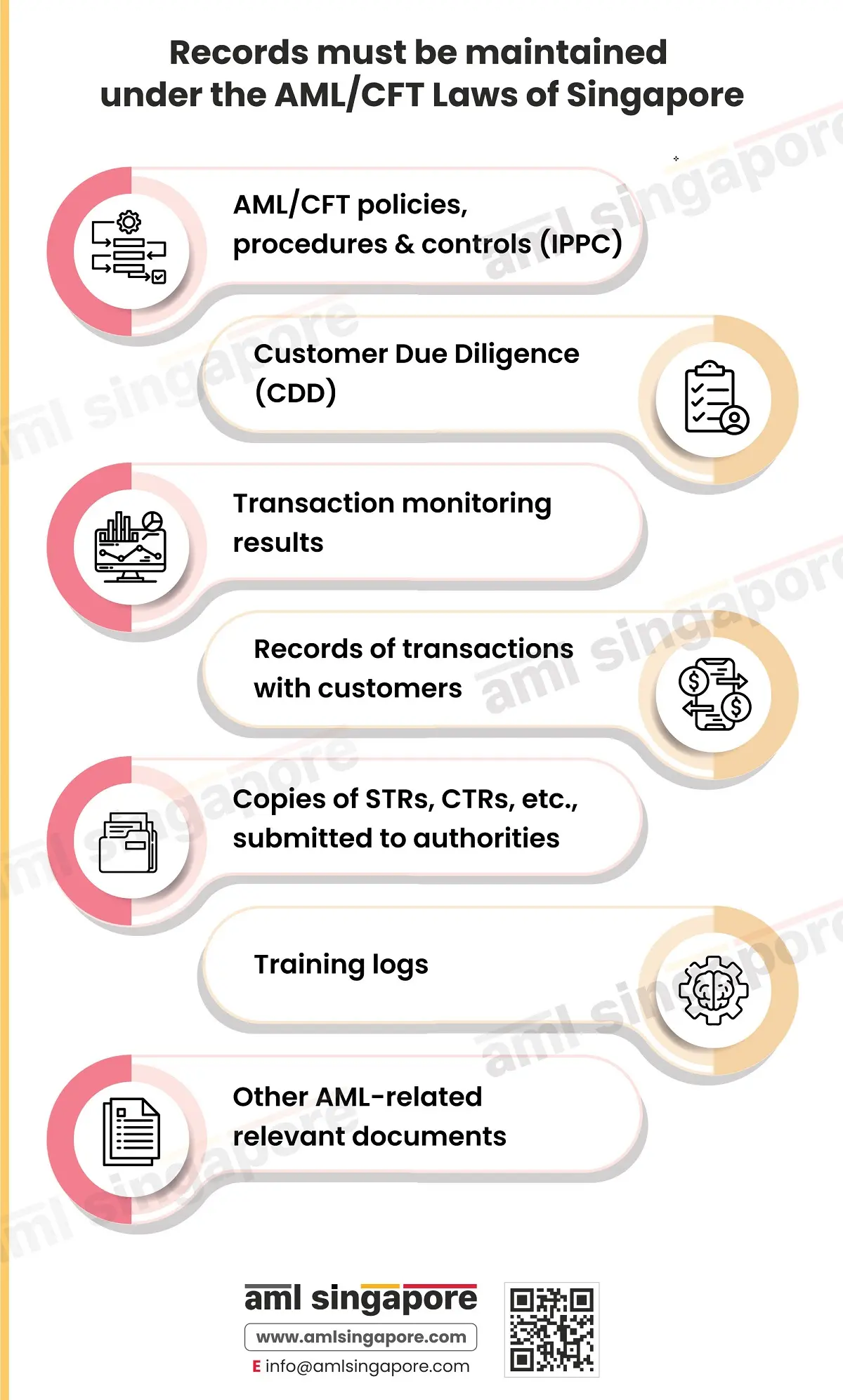
- AML/CFT policies, procedures and controls (IPPC)
- Customer due diligence (CDD)
- Transaction monitoring results
- Records of transactions with customers
- Copies of STRs, CTRs, and other reports submitted to MAS, STRO, and other relevant authorities like the Ministry of Law
- Training logs
- Other AML-related relevant documents
- Paper
- Electronic form
- On microfilm
The Singapore court of law may ask for these documents as evidence. You must create and maintain these records to submit them to the court when requested.
What records must be maintained under the AML/CFT Laws of Singapore?
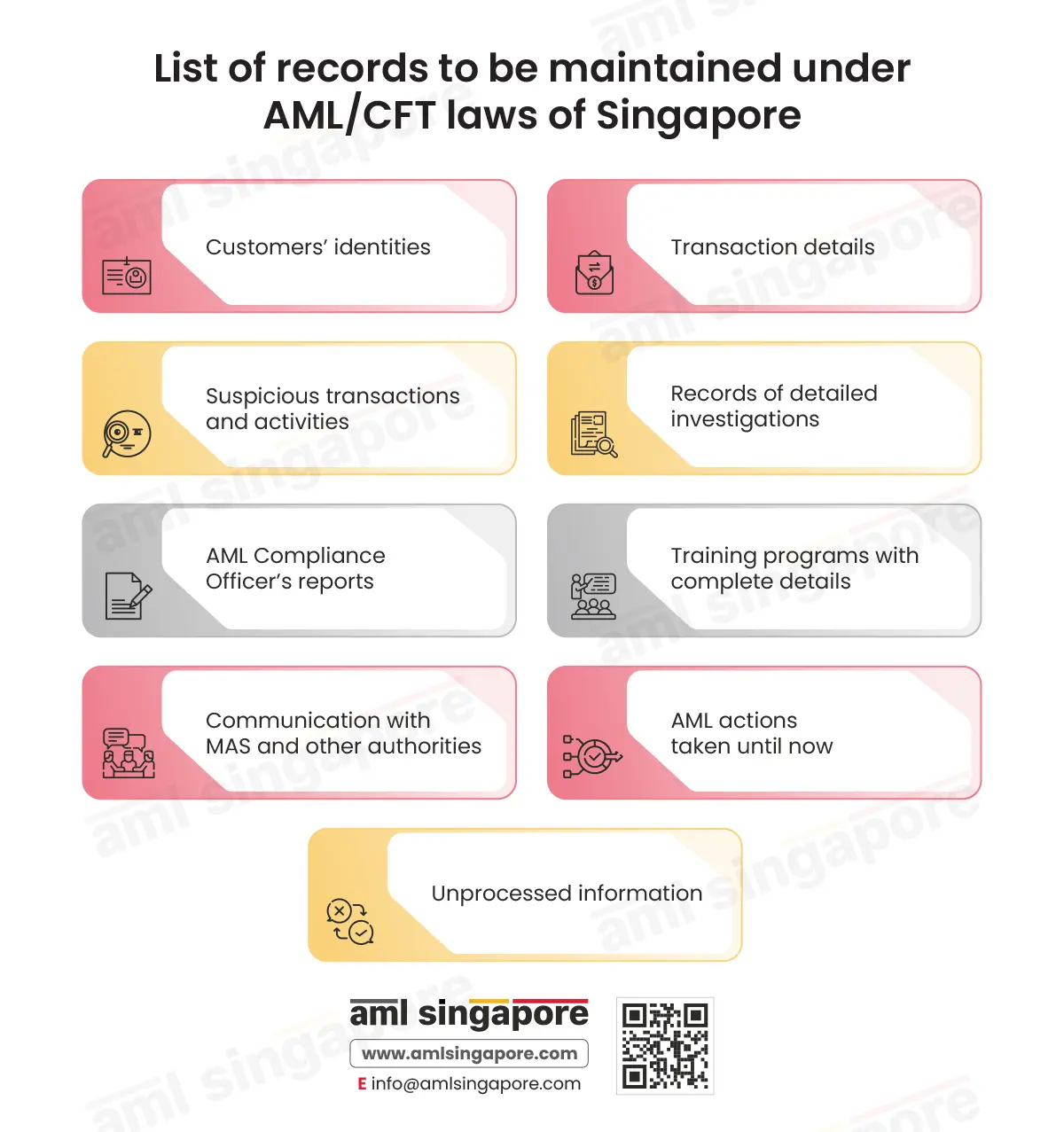
The law requires regulated entities to maintain records of the following:
Customers’ identities
You must collect information on individuals, such as names, dates of birth, addresses, and other details. Gather necessary documents to verify these details, like address proof and identity documents. For entities, you must find information on names, incorporation date, number of employees, beneficial owners, and other relevant data. You must also save your correspondence with customers on transactions, business relationships, and other matters.
You must save these data points on your individual and entity customers. And refer to them when needed before a transaction. Collecting these data points before forming a business relationship is essential. Results of customer screening against watchlists, PEPs, and sanctions are also vital.
Transaction details
It would be best if you tracked your transactions to avoid any possibility of money laundering. For this, you must collect data on each transaction, such as:
- Date of transaction
- Parties involved and their role
- Type of transaction
- Transaction value
- Taxes and charges involved
- Medium of payment
- Payment date
- Source of money or name of the sender
All these information points can serve as a good reference point in the future when you want to track it. Also, you can raise an alert if you spot something out of the ordinary. For example, it is suspicious if the payment value is enormous and the customer prefers an all-cash transaction.
Suspicious transactions and activities
Most of the effort for AML compliance is towards identifying suspicious transactions. You can stop,g prevent, or reduce their effects only when you identify them. So, it’s crucial to have records of these suspicious transactions.
Every regulated entity must understand what a suspicious transaction is in their field of operations. Like a sizeable cash-value transaction. Or a transaction with the involvement of an unknown third party. All these are different types of suspicious transactions found in different industries. You must make a list of all the possible transactions. Then, review your transactions and compare them to detect suspicious ones.
You must maintain records of such suspicious transactions and other related details. It helps you avoid similar transactions. Since you maintain records of all transactions, separate the suspicious transactions from that list and make another file. Analyse it properly to identify patterns or trends and make conclusions. Thus, these records can help you in your future decisions. Also, you need to report these to authorities.
Records of detailed investigations
When you identify suspicious transactions, some of them are false positives. But if those relate to high-risk customers, you must investigate further.
More investigations require you to collect more data from customers and other parties. You must maintain records of the extra data and information you analyse. Whatever evidence you get, save it. Such records help you determine whether the activity has linkages to money laundering.
If you want any third party or authority to investigate further, you can submit these records to help in their assessment.
AML Compliance Officer’s reports
Entities under the AML regime in Singapore must have a dedicated AML compliance team. This team must have a deserving AML compliance officer to manage all AML-related activities.
They will ensure the business complies with all the AML provisions in Singapore. For this, they will:
- Create AML framework, policies, procedures, and controls
- Manage the monitoring of transactions with customers
- Supervise risk assessments of customers and build risk profiles
- Conduct training for employees
- Ensure submission of reports to MAS and other authorities
You must maintain a copy of the reports the officer submits to the senior management and MAS. These records will help you refer to them for decision-making in the future. Also, these reports are a summary of the entity’s efforts for AML compliance. So, you must maintain them as records to assess your past performance and make plans.
Training programs with complete details
- Topics covered in training
- Number of participants
- Seniority level in the business
- Education and experience of participants
- Materials used
- Medium of training
Communication with MAS and other authorities
An often ignored aspect of record-keeping is all your communication with MAS. You must maintain its records until there is clarity on that aspect. Records of the following are necessary:
- Any requests for submissions of documents or reports from MAS and other authorities
- Any complaints raised by MAS on your AML compliance
- Your response to MAS on their complaints and their approval
- Any requests/queries, or doubts submitted by you to MAS
These will help you get confirmation on your AML compliance and work towards it better.
AML actions taken until now
MAS and other relevant AML authorities in Singapore expect AML compliance from you. In this race, they supervise your AML efforts. They review your AML compliance and recommend remediation measures to you.
In response to these recommendations, you must act to comply with AML regulations. For every action taken by you, you must maintain records of it. You must give details on the recommendation action taken and its impact on your business. You must also attach the audit reports on your AML compliance efforts.
These records are essential to know your actions in response to MAS’s supervisory engagement. Also, it proves that you are working towards complying with all provisions of AML laws.
Unprocessed information
Suppose you conduct investigations on customers or transactions that later turn out to be non-suspicious. That means the customer or transaction is legal, and you did not find any trace of money laundering. It does not mean that you delete the records of such investigations.
You must maintain proper records of such transactions and customers who were initially suspicious but later found non-suspicious.
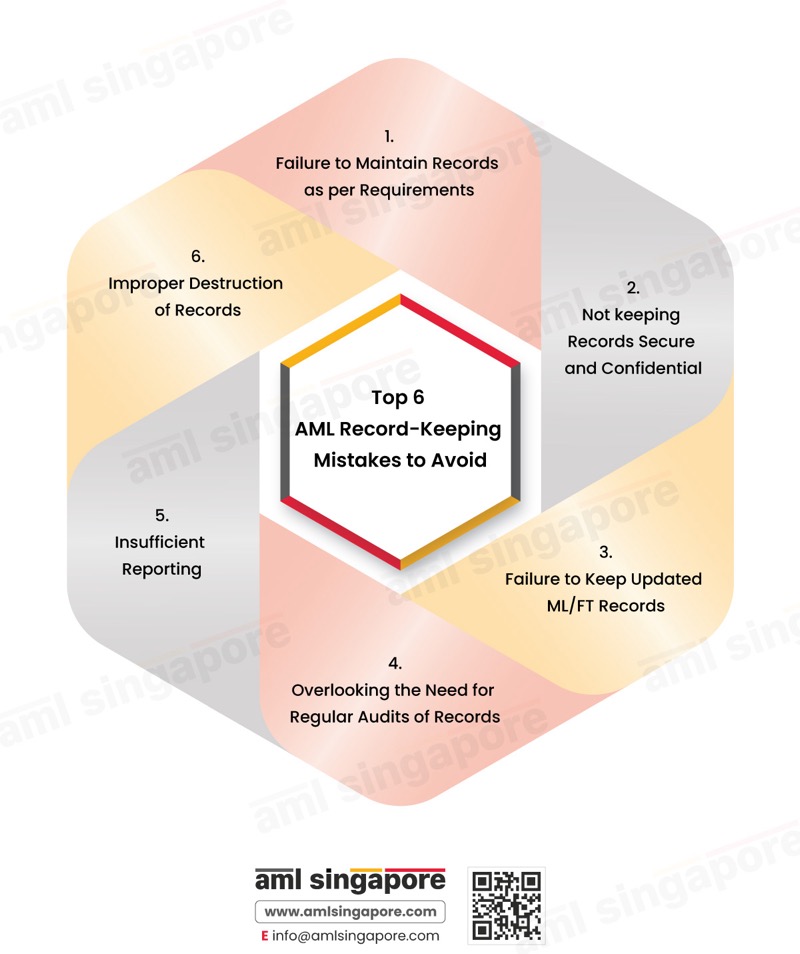
Top 6 AML record-keeping mistakes to avoid
The above section explains the various types of records you must maintain for AML compliance. While creating and maintaining these records, adopt the global best practices. You must avoid the following mistakes to keep your records relevant for your business and Singaporean authorities:
1. Failure to maintain records per requirements
It’s the age of technology. Generally, companies maintain records in the AML KYC Software. This ensures complete and accurate records. Also, you can be sure of their safety and security. You can keep these records confidential by managing permissions for accessibility. Also, such software solutions allow analytics and insights generation, leading to better decision-making and compliance.
In Singapore, you must maintain records in originals and copies in paper, digital, or microfilm formats. So, you must maintain these records in these forms.
2. Not keeping records secure and confidential.
Data confidentiality is a serious issue. There are chances of data theft by internal employees or external hacking. So, make it a practice to protect all your sensitive data.
In the case of AML, generally, you have data on customers and transactions. Any theft of this data leaks customer information and payments-related materials. So, you must encrypt the data to keep it secure. Also, permit only a few trustworthy personnel to access data.
3. Failure to keep updated ML/FT records
Constant changes occur in AML compliance requirements. Even organisations undergo changes in operations, processes, data, and other aspects. So, all these amendments must have equal adjustments in records as well.
You can’t keep your records outdated. So, update them according to the changes in your business. If you keep them up-to-date, there are higher chances of easy and smooth compliance. So, don’t forget to update your records as and when new changes come.
4. Overlook the need for regular audits of records.
Your records might have some errors or loopholes. Also, the record-keeping processes can have deficiencies or gaps. These deficiencies can lead to inaccurate or incomplete records, affecting your AML compliance. So, it is crucial to pay attention to audits of your records and record-keeping processes.
You can set a schedule for regular internal audits. You can identify errors and rectify them to improve their quality and efficiency. Also, you can set an annual external audit by an AML auditor to get an outside perspective on your record-keeping procedures. These records must meet regulatory standards and help you comply with them.
5. Insufficient reporting
You are maintaining records of customers and their identities. You also have records of transactions in value and volume and related aspects. You maintain all these records to help you with AML compliance.
What happens when you detect some red flags in records? Or some strange activity, different from the usual? You report it to authorities. This is what you are supposed to do with records. Whenever you spot something unusual, report it to senior management or regulatory authorities. These records help you create reports to submit to authorities according to Singaporean reporting requirements.
6. Improper destruction of records
According to Singaporean AML regulations, you must maintain these records for five years. After five years, you can destroy them unless MAS asks you not to destroy specific records.
But while destroying these records, ensure it happens properly and securely. Use a solution to ensure permanent deletion from electronic sources. If those are paper records, you can shred them to destroy every part of the paper. Whatever way you use, ensure there is no trace left.
How can AML Singapore help you?
You know the various records you must maintain for AML compliance in Singapore. These records will act as evidence of a successful AML compliance program. Also, the investors and senior management feel confident about the entity’s AML efforts after seeing these records. So, avoid these basic pitfalls in record-keeping to ensure up-to-date, accurate, and complete records.
If you need help designing your record-keeping procedures, hire an expert AML consultant like AML Singapore.
AML Singapore is a leading AML consultant in Singapore. We help with this fundamental task of proper record-keeping. Our expert AML professionals ensure you stay safe from the legal repercussions of AML non-compliance. We also regularly audit these records to check for gaps and inconsistencies. Besides AML compliance, it helps you with operational efficiency and financial management.
So, give record-keeping the importance it deserves and adopt its best practices.

Ready to take your AML compliance to the next level?
Empower your business with our record-keeping practices.
About the Author
Pathik Shah
FCA, CAMS, CISA, CS, DISA (ICAI), FAFP (ICAI)
Pathik is a Chartered Accountant with more than 26 years of experience in governance, risk, and compliance. He helps companies with end-to-end AML compliance services, from conducting Enterprise- Wide Risk Assessments to implementing the robust AML Compliance framework. He has played a pivotal role as a functional expert in developing and implementing RegTech solutions for streamlined compliance.